15.9 过早变化率
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言Consider a car driving down the highway and think about its speed. You are probably thinking about speed in terms of going a given distance in a given amount of time. The units could be miles per hour or feet per second, but the units always have time in the denominator. What happens when you consider the instantaneous speed of the car at one instant of time? Wouldn't the denominator be zero?
::考虑一下开下高速公路的汽车,然后考虑一下它的速度。你可能考虑的是速度,在一定的时间内去一个特定距离的速度。单位可以是每小时英里或每秒英尺,但单位总是有时间的分母。当你一瞬间考虑汽车的瞬时速度时会发生什么呢?分母不是零吗?
Insta ntaneous Rate of Change
::过早变化率When you first learned about slope, you learned the mnemonic device "rise over run" to help you remember that to calculate the slope between two points, you use the following formula:
::当你第一次学会关于斜坡, 你学会了“ 向上倾斜” 的内温设备, 来帮助您记住, 要计算两个点之间的斜坡, 您使用以下公式 :
::my2 - y1x2 - x1 。In calculus, you learn that for curved functions, it makes more sense to discuss the slope at one precise point rather than between two points. The slope at one point is called the slope of the tangent line, and the slope between two separate points is called a secant line.
::在微积分中,您知道,对于曲线函数来说,在一个精确点而不是两个点之间讨论斜坡比较合理。一个点的斜坡称为正切线的斜坡,两个分开点之间的斜坡称为偏移线。The average rate of change of a function is the slope of the secant line through two points. The instantaneous rate of change is the slope of the tangent line at a point.
::函数的平均变化率是分离线通过两点的斜坡。瞬时变化率是点对齐线的斜坡。The slope at a point (the slope of the tangent line) can be approximated by the slope of secant lines as the "run" of each secant line approaches zero.
::P点的斜坡(正切线的斜坡)可被偏移线的斜坡所近似,即每偏移线的“运行”接近零。Because you are interested in the slope as the "run" approaches zero, this is a limit question. One of the main reasons you study limits in calculus is so you can determine the slope of a curve at a point (the slope of a tangent line).
::因为您对“ 运行” 接近零时的斜坡感兴趣, 因此这是一个限制问题。 您研究微积分限制的主要原因之一是您可以在某个点( 切线的斜坡) 确定曲线的斜坡 。A derivative function is the function of the slopes of the tangent lines of the original function.
::衍生函数是原函数正切线的斜坡函数。The following video discusses the g raphical approach to average and instantaneous rate of change:
::以下影片讨论平均和即时变化率的图形方法:Play, Learn, and Explore Average and Instantaneous Rate of Change:
::玩耍、学习和探索平均和不时变化率:Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Estimate the slope of the following function at -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, and 3. Organize the slopes in a table.
::以下函数的斜坡估计值为-3、2-2、-1、0、1、2和3。Solution:
::解决方案 :By mentally drawing a tangent line at the following -values, you can estimate the following slopes:
::通过在精神上按照以下x值绘制正切线,您可以估计以下坡度:slope -3 0 -2 0 -1 -1 0 -1 1 2 2 0 3 0 If you graph these points, you will produce a graph of what's known as the derivative of the original function.
::如果您将这些点图解出来, 您将会生成一个图形, 显示原始函数的衍生物 。Example 2
::例2Estimate the slope of the function at the point by calculating four successively close secant lines.
::在点(1,1)计算四条相接分离线时,估计函数f(x)=x的斜度。Solution:
::解决方案 :Calculate the slope between and four other points on the curve:
::计算曲线上(1,1)和4个其他点之间的斜度:The slope of the line between and is
:5,5)和(1,1)之间线的斜坡为m1=5-15-1-1-0.309。
The slope of the line between and is
::在(4,2)和(1,1)之间线的斜坡为m2=2-14-10.333。The slope of the line between and is
::在(3,3)和(1,1)之间线的斜坡是m3=3-13-10.366。The slope of the line between and is
::在(2,2)和(1,1)之间线的斜坡为m1=0.73-10.7-12.19。An estimate for the slope of the function at the point would be .
::点(1,1)的函数 f(x) =x 的斜度估计数为 . 45。Example 3
::例3Evaluate the following limit and explain its connection with Example 2:
::评估以下限度并解释其与实例2的联系:
::limx%1 (x- 1x- 1)Solution:
::解决方案 :Notice that the pattern in the previous problem is leading up to . Unfortunately, this cannot be computed directly because there is a zero in the denominator. Luckily, you know how to evaluate using limits.
::请注意上一个问题的模式导致1-11-1。 不幸的是,这无法直接计算,因为分母为零。 幸运的是,你知道如何评估使用限值。
::m=limx%1 ((x-1)(x-1)(x-1)(x-1)(x+1)(x+1)))=limx%1 ((x-1)(x-1)(x+1)(x+1)))=limx%1(1(1(x+1)(1)(1)(11+1=12=0.5)The slope of the function at the point is exactly .
::点(1,1)的函数 f(x)=x的斜度为 m=12。Example 4
::例4Recall the question from the Introduction: What happens when you consider the instantaneous speed of a car driving down the highway at one instant of time?
::回顾导言中的问题:如果考虑到一瞬间一辆汽车在高速公路上行驶的瞬时速度,会发生什么情况?Solution:
::解决方案 :Write the ratio of distance to time and use limit notation to allow time to go to zero. Notice that you get a zero in the denominator.
::写入距离与时间的比率, 并使用限制的标记, 以便允许时间到零。 请注意, 您的分母中位数为零 。
::平时0( 远距离时间)The great thing about limits is that you have learned techniques for finding a limit even when the denominator goes to zero. Instantaneous speed for a car essentially means the number that the speedometer reads at that precise moment in time. You are no longer restricted to finding slope from two separate points.
::限制的伟大之处在于您已经学会了在分母变为零时寻找极限的技术。 汽车的即时速度基本上意味着在那个精确时刻速计读取的数字。 您不再局限于从两个不同的点上找到斜坡。Example 5
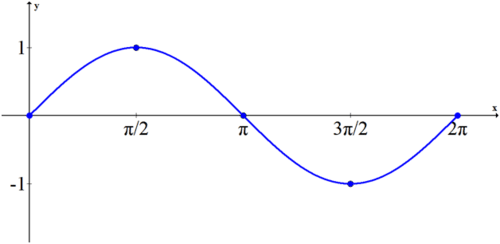
::例5Sketch a complete cycle of a sine function . Estimate the slopes at
::绘制一个正弦函数的完整周期。 估计斜坡为 0,%2, , 32, 和 22 。Solution:
::解决方案 :Slope 0 1 0 -1 0 1 Notice that these are the exact values of cosine evaluated at those points.
::请注意,这些是在这些点上评估的余弦的准确值。Example 6
::例6Logan travels by bike at 20 mph for 3 hours. Then she gets in a car and drives 60 mph for 2 hours. Sketch both the distance vs. time graph and the rate vs. time graph.
::罗根乘自行车在20海里处旅行3小时,然后她乘车驾驶60英里,2小时。Solution :
::解决方案 :Distance vs. Time:
::距离与时间 :
Rate vs. Time: (This is the graph of the derivative of the original function shown above.)
::率与时间这是上面显示的原函数的衍生物图 。 )

Example 7
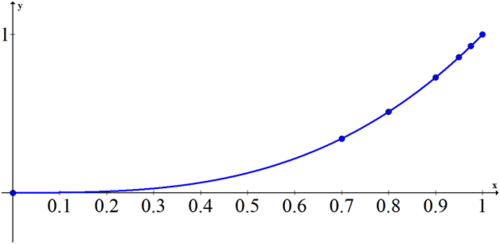
::例7Approximate the slope of at by using secant lines from the left. Will the actual slope be greater or less than the estimates?
::使用左侧的分隔线,接近 y=x3 的斜坡(1,1) 。 实际的斜坡会大于还是小于估计值?Solution :
::解决方案 :The slope of the line between and is
::线(0.7,0.73)和(1,1)之间的斜坡为m1=0.73-10.7-12.19。The slope of the line between and is
::在(0.8,0.83)和(1,1)之间线的斜坡为m2=0.83-10.8-12.44。The slope of the line between and is
::在(0.9,0.93)和(1,1)之间线的斜坡为m3=0.93-10.9-12.71。The slope of the line between and is
::在(0.95,0.953)和(1,1)之间线的斜坡为m1=0.953-10.95-11.8525。The slope of the line between and is
::在(0.975,0.9753和(1,1)之间线的斜坡为m1=0.9753-10.975-12.925625。The slope at will be slightly greater than the estimates because of the way the slope curves. The slope at appears to be about 3.
::由于坡度曲线的方式,(1,1)的坡度将略高于估计数。(1,1)的坡度似乎约为3。Summary
::摘要-
A
secant line
is a line that passes through two distinct points on a function.
::秒线是指通过函数上两个不同点的行。 -
The
average rate of change
of a function is the slope of the secant line through two points.
::函数的平均变化速率是通过两个点的分隔线坡度。 -
A
tangent line
is a line that passes through one point on a function.
::相切线是函数通过一个点的线条。 -
The
instantaneous rate of change
is the slope of the tangent line at a point.
::瞬时变化率是某一点相切线的斜坡。 -
A
derivative
function
is a function of the slopes of the original function.
::衍生函数是原函数的斜坡函数。
Review
::回顾1. Approximate the slope of at by using secant lines from the left. Will the actual slope be greater or less than the estimates?
::1. 使用左侧的分隔线,接近y=x2(1,1)的斜坡。 实际斜坡是大于还是小于估计数?2. Evaluate the following limit and explain how it confirms your answer to Number 1:
::2. 评价以下限度,并解释如何证实你对第1号的答复:
::limx%1 (x2- 1x- 1)3. Approximate the slope of at by using secant lines from the left. Will the actual slope be greater or less than the estimates?
::3. 使用左侧偏移线(1,4)接近y=3x2+1的斜坡(1,4),实际斜坡是大于还是小于估计数?4. Evaluate the following limit and explain how it confirms your answer to Number 3:
::4. 评价以下限制,并解释如何证实你对第3号的答复:
::limx%1( 3x2+1- 4x- 1)5. Approximate the slope of at by using secant lines from the left. Will the actual slope be greater or less than the estimates?
::5. 使用左侧的分离线,接近y=x3-2(1,-1)的斜坡。实际斜坡是大于还是小于估计?6. Evaluate the following limit and explain how it confirms your answer to Number 5:
::6. 评价以下限制,并解释如何证实你对第5号的答复:
::立方公尺x1(x3--2)-(--1)x-17. Approximate the slope of at by using secant lines from the left. Will the actual slope be greater or less than the estimates?
::7. 在(1,1)时使用左侧的分隔线,接近y=2x3-1的斜坡。实际斜坡是大于还是小于估计?8. What limit could you evaluate to confirm your answer to Number 7?
::8. 为了确认你对7号的回答,你能评估什么限度?9. Sketch a complete cycle of a cosine function . Estimate the slopes at
::9. 绘制一个余弦函数的完整周期,估计斜坡为0,2,2,3,2,2和2。10. How do the slopes found in the previous question relate to the sine function? What function do you think is the derivative of the cosine function?
::10. 上一个问题中发现的斜坡与正弦函数有何关系?你认为余弦函数的衍生函数是什么?11. Sketch the line . What is the slope at each point on this line? What is the derivative of this function?
::11. 将 y=2x+1 线平铺成一条线。 这条线上每个点的斜坡是什么? 此函数的衍生物是什么?12. Logan travels by bike at 30 mph for 2 hours. Then she gets in a car and drives 65 mph for 3 hours. Sketch both the distance vs. time graph and the rate vs. time graph.
::12. 洛根乘自行车在30海里处旅行2小时,然后她乘车驾驶65英里处3小时。13. Explain what a tangent line is and how it relates to derivatives.
::13. 解释何为不相干线及其与衍生物的关系。14. Why is finding the slope of a tangent line for a point on a function the same as the instantaneous rate of change at that point?
::14. 为什么在某一函数上找到与该点瞬时变化率相同的点的正切线斜坡?15. What do limits have to do with finding the slopes of tangent lines?
::15. 界限与寻找相左线的斜坡有什么关系?Review (Answers )
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
A
secant line
is a line that passes through two distinct points on a function.