2.3 矩阵矢量方程式Ax=b
章节大纲
-
In the last lesson we talked about solving systems of linear equations and how that related to finding and taking linear combinations of vectors.
::在最后一堂课上,我们谈到解决线性方程式系统的问题,以及这与寻找和采用矢量线性组合的关系。We saw that we could take the linear system of equations , take the coefficients of each variable and put them into a vector. We would end up with an equation like [ a 1 a 2 a 3 ] x 1 + [ b 1 b 2 b 3 ] x 2 + [ c 1 c 2 c 3 ] x 3 = [ d 1 d 2 d 3 ] . Now we went over this briefly, but we could end up writing this as a matrix vector product. This comes out to be [ a 1 b 1 c 1 a 2 b 2 c 2 a 3 b 3 c 3 ] ⋅ [ x 1 x 2 x 3 ] = [ d 1 d 2 d 3 ] which is of the form A → x = → b .
::我们发现我们可以采用线性方程系统, 将每个变量的系数取入到矢量中。 我们最后会使用一个方程, 如[a1a2a3]x1+[b1b2b3]x2+[b1b2b3]x2+[c1c2c3]x3=[d1d2d3]。 现在我们简短地讨论了这个方程, 但我们最终可以写成一个矩阵矢量产品。 这个方程是[a1b1c1c1a2b2c2c2c2a3b3c3]}[x1x2x3]=[d1d2d3], 形式为Axb。
Now we see that solving a system of linear equations can be done by multiplying both sides of the equation by A − 1 to get → x = A − 1 → b . Now, don't fret, solving this does not turn out to be that simple, because we end up getting several cases we have to work with.
::现在我们看到,解决线性方程式系统的方法是将方程式的两边乘以 A-1 以获得 x= A-1 b。现在,不要担心,解决这个问题并不那么简单,因为我们最终要处理几个案例。Remember, we can only take the inverse of a matrix that is square so it has to be an n × n dimensional matrix. This means a system with an unequal amount of variables and equations does not have a unique solution or maybe not any solution for that matter.
::记住, 我们只能接受正方矩阵的反向, 所以它必须是一个 nxn 维矩阵。 这意味着一个变量和方程式数量不均的系统, 没有独特的解决方案, 或者没有解决方案 。If there are more variables than there are equations then there are infinite solutions because we will have several free variables as a result. If there are more equations then variables we will likely get no solutions, but in some cases we can get a consistent system with one or infinitely many solutions if multiple equations or all equations are the same and just off by a scalar multiple.
::如果变量比方程式多,那么就会有无限的解决方案,因为我们因此会有一些自由变量。如果有更多的方程式,那么变量就很可能得不到任何解决方案,但在某些情况下,如果多个方程式或所有方程式相同,并且只是用一个斜体倍数关闭,我们就可以获得一个一致的系统,一个或无限多的解决方案,在某些情况下,我们可以得到一个一致的系统,如果多个方程式或所有方程式相同,并且只是用一个斜体倍数关闭。
Now, when we take the inverse we may also have the case of the matrix being square, but not invertible (because of 0 determinant). Then when the matrix is not invertible the columns must be linearly dependent , which means there will be one vector in their span of the others. In other words we have an n × n matrix that is not invertible it means that the span of the columns is not R n , hence linearly independent .
::现在,当我们采取逆向矩阵时,我们可能也会看到矩阵是正方的,但不可倒置(因为0个决定因素 ) 。 当矩阵不是倒置时, 列必须是线性依赖的, 这意味着在其它矩阵的间距内会有一个矢量。 换句话说, 我们有一个nxn矩阵, 而不是不可倒置, 这意味着列的宽度不是Rn, 也就是说线性独立 。Now just because the col umns of the matrix are linearly independent does not mean that the equation has no solution. For instance, if our matrix spans a plane in 3 dimensions then there exist solutions for some vectors → b , it is just harder to find it.
::现在,仅仅因为矩阵的列线是线性独立的,并不意味着方程式没有解决办法。例如,如果我们的矩阵横跨一个平面的3维,那么某些矢量 'b' 就有解决办法,那么找到它就更困难了。First, let's try an example with a consistent system of equations.
::首先,我们来举个例子,用一个一致的方程式系统。Take the system:
::采用以下系统:x 1 + 4 x 2 − 3 x 3 = − 17 − 2 x 1 − 5 x 2 + 6 x 3 = 32 6 x 1 + 15 x 2 + 18 x 3 = 100
::x1+4x2-3x317-2x1-5x2+6x3=326x1+15x2+18x3=100First, let's put it in the matrix vector product form
::首先,让我们把它放在矩阵矢量产品表格中[ 1 4 − 3 − 2 − 5 6 6 15 18 ] ⋅ [ x 1 x 2 x 3 ] = [ − 17 32 100 ] .
::[14] [x1x2x3] =[-173210]。Obviously we can apply row reduction, but let's multiply but the inverse of the matrix. First, take the inverse of the matrix. We're going to use a technique we'll study more in depth in chapter 3, but if you don't follow it, watch this video.
::显然,我们可以使用减排法,但是让我们乘以矩阵的反面。 首先,选择矩阵的反面。 我们将使用一种技术,我们将在第3章中更深入地研究, 但是如果你不遵循, 请看这个视频。First, we must take the Adj ( A ) which is achieved by taking the minor and then multiplying by ( − 1 ) i j .
::首先,我们必须采取Adj(A),这是通过带走未成年人而实现的,然后乘以(-1)ij。First A d j ( A T ) ( 1 , 1 ) = det ( [ − 5 6 15 18 ] ) = − 90 − 90 = − 180
::第一次Adj(AT) 1,1=det([-561518]) 90-90180Then A d j ( A T ) ( 1 , 2 ) = det ( [ − 2 6 6 18 ] ) = − 36 − 36 = − 72
::然后Adj(AT) 1,2=det([ - 26618]) 36-3672And going on and on...
::一直不停地说下去...A d j ( A T ) ( 1 , 3 ) = det ( [ − 2 − 5 6 15 ] ) = − 30 − ( − 30 ) = 30 − 30 = 0
::Adj(AT)(1,3,3)=det([-2-5615]) 30-(-)-(-)=30-30=0A d j ( A T ) ( 2 , 1 ) = det ( [ 4 − 3 15 18 ] ) = 72 − ( − 45 ) = 117
::Adj(AT)(2,1)=det([4-31518])=72-(-45)=117A d j ( A T ) ( 2 , 2 ) = det ( [ 1 − 3 6 18 ] ) = 18 − ( − 18 ) = 36
::Adj(AT)(2,2,2)=det([1-3618])=18-(-18)=36A d j ( A T ) ( 2 , 3 ) = det ( [ 1 4 6 15 ] ) = 15 − 24 = − 9
::Adj(AT)(2,3)=det([14615])=15-249A d j ( A T ) ( 3 , 1 ) = det ( [ 4 − 3 − 5 6 ] ) = 24 − 15 = 9
::Adj(AT)(3,1)=det([4-3-56])=24-15=9A d j ( A T ) ( 3 , 2 ) = det ( [ 1 − 3 − 2 6 ] ) = 6 − 6 = 0
::Adj(AT)(3,2)=det([1-3-26])=6-6=0A d j ( A T ) ( 3 , 3 ) = det ( [ 1 4 − 2 − 5 ] ) = − 5 − ( − 8 ) = 3
::Adj(AT)(3,3)=det([14-2-5])5-(8)=3Now we get adding all of this up
::现在我们可以把Adj(A)=(-1)i+j[-180-72011736-9903]T=[-180720-1176990-3]
::最后,我们得出A-1=1detA[-180720-1176990-3]T的反比。
::现在计算A的决定因素
::=156151842661832515(-180)-4(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-0)-(-)-3(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)-(-)
::A-1=1108[- 180720- 11736990-3]=[-53-131212331300112-136]
::然后解决这个系统,我们终将面对→ x = [ − 5 3 − 13 12 1 12 2 3 1 3 0 0 1 12 − 1 36 ] ⋅ [ − 17 32 100 ] = [ 2 − 2 3 49 9 ]
::x=[-53-1312112231300112-136]][-1732100]=[2-23499]Hence x 1 = 2 , x 2 = − 2 3 , x 3 = 49 9
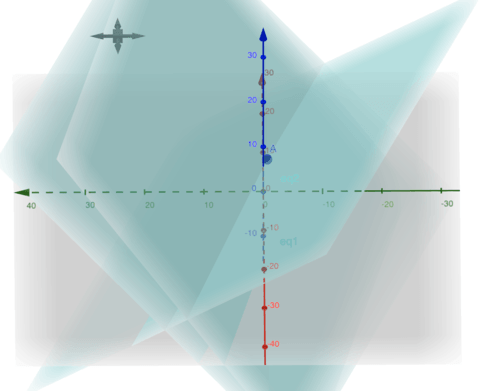
::因此 x1 = 2, x2 23, x3 = 499Now let's look at this geometrically to get
::现在让我们看看这个几何式的
Let's do another example:
::让我们再举一个例子:[ 1 2 3 − 1 5 4 3 − 7 − 4 ] ⋅ [ x 1 x 2 x 3 ] = [ 6 8 − 8 ]
::[123-1543-7-7-4]][x1x2x3]=[68-8]Let's try to take the inverse of this matrix. First, before we get to far let's check the value of the determinant to make sure the matrix is invertible.
::让我们尝试逆向这个矩阵。首先,在我们到达远方之前, 让我们检查一下决定因素的价值, 以确保矩阵是不可倒置的。det ( [ 1 2 3 − 1 5 4 3 − 7 − 4 ] ) = 1 | 5 4 − 7 − 4 | − 2 | − 1 4 3 − 4 | + 3 | − 1 5 3 − 7 | = 8 + 16 − 24 = 24 − 24 = 0
:[123-1543-7-4])=154-7-42143-43153-78+16-24=24-24=0
So sadly, the determinant has value zero and the matrix is not invertible. We see we cannot take the inverse of the matrix because the columns are linearly dependent. The sum of the first two columns equals the third column, [ 1 − 1 3 ] + [ 2 5 − 7 ] = [ 3 4 − 4 ] .
::令人痛心的是,决定因素的值为零,而矩阵是不可倒置的。我们看到我们不能对矩阵的反向,因为列是线性依附的。前两列的总和等于第三列,[1-13]+[25-7]=[34-4]。However, this does not tell us that there is no solution. We see that there is a linear dependence relation allowing us to eliminate the third vector and then we can check if [ 6 8 − 8 ] is in the span of those two vectors.
::然而,这并没有告诉我们没有解决办法。我们看到存在着一种线性依赖关系,使我们能够消灭第三种向量,然后我们可以检查[68-8]是否在这两种向量的范围之内。We want to see if there exists x1 and x2 such that [ 1 − 1 3 ] x 1 + [ 2 5 − 7 ] x 2 = [ 6 8 − 8 ] . So let's try to see if there exists a unique solution to the system of equations
::我们想看看是否存在 x1 和 x2, 这样[ 1- 13] x1+[ 25-7]x2=[ 68-8] 。 因此,让我们尝试看看是否对方程系统有一个独特的解决方案 。x 1 + 2 x 2 = 6 − x 1 + 5 x 2 = 8 3 x 1 − 7 x 2 = − 8
::x1+2x2=6-x1+5x2=83x1-7x2=8even though there are more equations than variables.
::尽管方程比变量多。Solving the first two equations we can add the first two equations elimination x 1 to get 7 x 2 = 14 → x 2 = 2 . Plugging back in we get the solution to the first two solutions as x 1 = x 2 = 2 . Now let's see if this is a solution to the third equation and plugging in we get 3(2) - 7(2) = 6 - 14 = -8 so that is a solution. Hence there is a solution to our system of equations we get → x = [ 2 2 0 ] , and the third entry is 0 because it is linearly dependent of the other two columns. However, there exists more than one solution, because we could also have → x = [ 1 1 1 ] because the sum of the first two columns equals the third column. From this wee see that there are infinite solutions, because [ 1 − 1 3 ] x 1 + [ 2 5 − 7 ] x 2 + [ 3 4 − 4 ] x 3 = [ 6 8 − 8 ] then subtracting the vector that x 3 multiplies you get [ 1 − 1 3 ] x 1 + [ 2 5 − 7 ] x 2 = [ 3 4 − 4 ] ( 2 − x 3 ) and because here x 1 and x 2 are going to be what they were to get the vector without the scalar coefficient and then multiplied by 2 − x 3 and because x 3 can be anything we have infinite solutions.
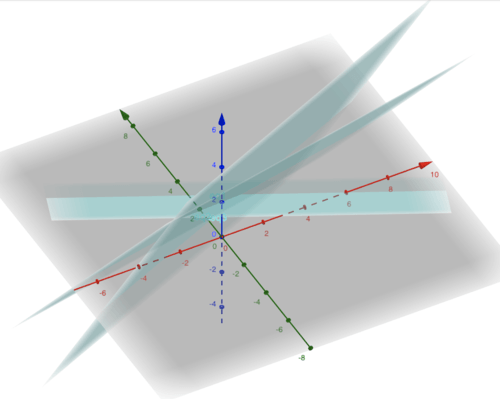
::解决前两个方程前两个方程式, 我们可以添加前两个方别删除 x1, 以获得 7x2= 14xxxxx2=2 。 插入后, 我们可以得到前两个方方的解决方案 7x2= 14x2= 2 。 现在让我们看看这是否是第三个方方方方的解决方案, 插入后, 3(2) - 7(2)= 6 - 7(2)= 6 - 14= 4= - 8, 这样就是一个解决方案。 因此, 我们的方程系统有一个解决方案, 我们得到 x=x=[ =[220], 第三个条目是0, 因为它与其他两列的直线依赖。 但是, 存在一个以上的解决方案, 是因为我们也可以有 x=[x=1]x1x1+[25-7]x2+[34-44]x3=[68- 8]x3=[34-4]x3x3x3, 3x2x2xxxxxx3], 因为2xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, , , , , , , , xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, , , , , , 和xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, , , x, , , xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, , , , , xxxxxxxxxxxx, , xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, 和xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx, x, x, 和xxxxxxx,Now geometrically we get a picture in the form of a line of intersection to get
::现在几何形形的我们得到一幅图片 以十字路口的形式giving us a line.
::给我们一条线。
Now, let's try one more example. Take the system of linear equations
::现在,让我们再举一个例子。 以线性方程系统为例3 x 1 − 4 x 2 + 7 x 3 = 12 − 6 x 1 + 8 x 2 − 14 x 3 = − 22 1.5 x 1 − 2 x 2 + 3.5 x 3 = 16
::3x1 - 4x2+7x3=12 - 6x1+8x2 - 14x3\\221.5x1 - 2x2+3.5x3=16Then we can put this into an matrix vector equation of the form A → x = → b which is [ 3 − 4 7 − 6 8 − 14 1.5 − 2 3.5 ] ⋅ [ x 1 x 2 x 3 ] = [ 12 − 22 16 ] which turns to the augmented matrix [ 3 − 4 7 ∣ 12 − 6 8 − 14 ∣ − 22 1.5 − 2 3.5 ∣ 16 ] .
::然后,我们可以将它放入一个矩阵矢量方程式,表A*xb为[3-47-68-141.5-23.5] 和[x1x2x3] =[12-2216] ,该方程式是扩充后的矩阵[3-47] 12-68-14221.5-23.5}16]。First, let's try to take the inverse of our matrix A (the one furthest to the left in the matrix vector equation). Now, take the determinant to make sure that the matrix is invertible.
::首先,让我们尝试从我们的矩阵 A( 矩阵矢量方程左最远的矩阵 A) 反转。 现在, 选择决定因素以确保矩阵是不可倒置的 。det ( [ 3 − 4 7 − 6 8 14 1.5 − 2 3.5 ] ) = 3 | 8 14 − 2 3.5 | + 4 | − 6 14 1.5 3.5 | + 7 | − 6 8 1.5 − 2 |
:[3-47-68141.5-23.5])=3814-23.546141.57681.5-2
This comes out to 3 ( 8 ⋅ 3.5 + 28 ) + 4 ( − 6 ⋅ 3.5 − 14 ⋅ 1.5 ) + 7 ( 12 − 8 ⋅ 1.5 ) = 3 ( 56 ) + 4 ( − 42 ) + 7 ( 0 ) = 168 − 168 = 0 Hence, the matrix is not invertible. Now let's check if there is a solution.
::这显示为 3( 8-3.5+28)+4(- 6- 3.5- 14- 1.5)+7( 12-8- 8- 1.5) +3( 56)+4( 42)+7( 0) = 168- 168= 0Hence, 矩阵是不可忽略的。 现在让我们检查是否有解决方案 。Now we find the linear dependence relationship between the columns. By inspection we have column three is the first column plus negative one times the second column. So now we have to check if the [ 12 − 22 16 ] ∈ Span { [ 3 − 6 1.5 ] , [ − 4 8 − 2 ] } .
::现在我们发现列之间的线性依赖关系。通过检查,我们发现第三列是第一列,第二列是负1倍。所以现在我们必须检查一下[12-2216]{Span{[3-61.5],[-48-2]}。Now let's try to see if there exists a solution to the system
::现在让我们看看系统是否有解决方案3 x 1 − 4 x 2 = 12 − 6 x 1 + 8 x 2 = − 22 1.5 x 1 − 2 x 2 = 16
::3x1 - 4x2=12 - 6x1+8x2221.5x1 - 2x2=16solving you would end up getting an equation equation 0 to some other number which means that there is no solution, hence the vector → b is not in the span of the columns of A.
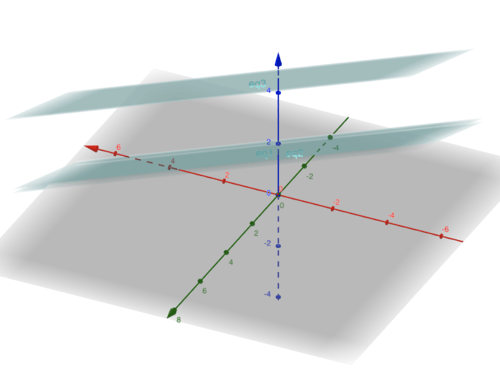
::解析最终会得到一个等式等式 0 到其他数字, 这意味着没有解决方案, 因此矢量 b 不在 A 列的横线内 。Looking at this geometrically we get parallel planes
::从几何角度看,我们得到平行的飞机
Let's make some conclusions about what we saw here:
::让我们就我们在这里看到的情况作出一些结论:Whenever we have a system that is expressed in the matrix form Ax = b, regardless of the dimensions of A, if A is not invertible then there either exists infinite solutions or no solutions. If the matrix is invertible then there is a unique solution. For the former case, to check if there is no solution you have to check if b is in the Span of the columns of A which is usually doable by inspection.
::当我们有一个以矩阵表Ax = b 表示的系统时,不管A的维度如何,如果A是不可倒置的,那么要么存在无限的解决方案,要么没有解决方案。如果矩阵是不可倒置的,那么就有一个独特的解决方案。对于前一种情况,要检查是否没有解决方案,您必须检查 A 列中是否有 b , 通常通过检查可以做到。
Here are some videos that will help you understand this better and runs through some more examples:
::以下是一些能帮助你更好理解的影片,