1.7 赤道模型介绍-interactive
章节大纲
-
The Purpose of this Lesson
::本课程的目的In this lesson you will develop a quadratic function to model a scenario involving constant acceleration. Quadratic functions can be represented with tables, equations, and graphs. Like linear and , quadratic functions are powerful models of real-world scenarios.
::在此教训中, 您将开发一个二次函数来模拟一个包含恒定加速的假设情景。 二次函数可以用表格、 方程式和图表来表示。 二次函数与线性函数和二次函数一样,是真实世界假设情景的强大模型。Introduction: Acceleration of a Car
::导言:加速驾驶车Piecewise functions can be used to model a car with a velocity that is different over different intervals. You will use a piecewise function here to approximate the position of a car that accelerates at a constant rate . You will then look more closely at the patterns in that model to develop an equation for a car that smoothly accelerates at a constant rate.
::小数函数可用于模拟速度不同间隔的汽车。 您可以在这里使用一个小数函数来估计以恒定速度加速的汽车的位置。 然后您将更仔细地查看该模型的图案, 以便为以恒定速度平稳加速的汽车开发一个方程式 。
Activity 1: Model Acceleration with a Piecewise Function
::活动1: 模型加速和一小片函数Example 1-1
::例1-1Laura is a professional formula racer. The top speed for her car is
::劳拉是一个专业的配方车赛车手。 她车的最高速度是每秒150米。 转换成每小时每英里。 与高速公路上典型的速度限制相比, 速度是多少倍? (提示:1英里大约是1.61公里)Laura is a professional formula racer Solution: Start by converting from meters per second to kilometers per hour
::解决办法:开始从每秒米转换为每小时150m1 s =1千千米/小时150m1 s =1 000 m 3600 s 1hr=540 km/小时
::1501平方米-1千米1000立方米-3600平方米1小时=540公里/小时Then convert from kilometers per hour to miles per hour
::然后从每小时公里转换为每小时英里
::540公里1赫拉1英里1.61公里
::540公里1赫拉1英里1.61公里That's almost 4 times as fast as the highest highway speed limit of 85 miles per hour!
::这几乎是时速85英里的最高高速公路速度限制的4倍!
::例1-2
::劳拉的车在赛跑时加速10米每秒。 这是什么意思? 为了支持你的解释,请举例说明她以1秒的标记、2秒的标记等速度行驶的速度。描述她的速度和时间之间的关系。找到速度的方程式是时间的函数 。Solution: An acceleration of 10 meters per second, per second, means that every second, she goes 10 meters per second faster. Here is a table showing her velocity at different times:
::解决方案:每秒加速10米,每秒加速10米,这意味着每秒,她速度每秒10米,速度更快。这里的表格显示她在不同时间的速度:t(秒)v(m/s)001110230330。
:秒)v (m/s)00100120330
The relationship between velocity and time is linear. As each second passes, the increase in velocity is a constant 10 meters per second. The equation relating velocity and time is:
::速度和时间之间的关系是线性。 每过一秒, 速度的增加是每秒10米的恒定值。 与速度和时间有关的方程式是: v=10t 。Example 1-3
::例1-3Laura wants to know how long it will take her to complete a 335 meter run of her upcoming race. She wants to create a piecewise function to approximate her distance as a function of time. She knows that she accelerates at 10 meters per second, per second. To simplify her model, she assumes that she travels at 10 meters per second for the entire 1st second, then 20 meters per second for the entire 2nd second, and so on. Here is a table showing the intervals of time and her corresponding velocity for that time.
::劳拉想知道她完成她即将到来的335米赛跑需要多长时间。 她想创建一个小字节功能, 以近似距离作为时间函数。 她知道她每秒加速10米。 她知道她每秒加速10米。 为了简化她的模型, 她假设她整个一秒以每秒10米的速度行走, 然后整个二秒以每秒20米的速度行走, 等等。 下面是一张显示时间间隔及其相应速度的表格 。-
Complete the table with her total completed distance at the end of each interval.
::填满表格时,每间距结束时她的完全完全距离。 -
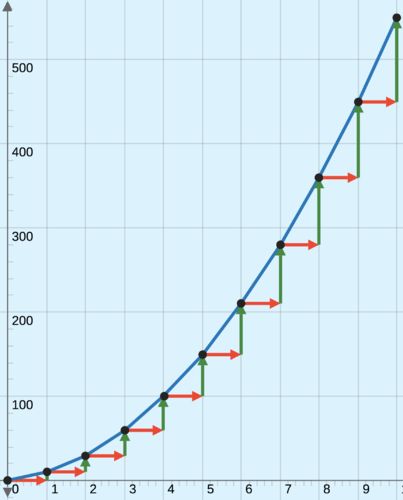
Create a graph which shows her distance as a function of time, connecting the points from the table with straight segments. What does the
over each interval signify?
::创建图表, 显示她的距离是时间函数, 将表格上的点与直线段连接起来。 每个间隔间距代表什么 ? -
Identify patterns in the table and the graph. Use your model to approximate when Laura passes the 335 mark. Why is this model only an approximation?
::识别表格和图表中的图案。 使用您的模型来估计劳拉通过335标记时的大致值。 为什么这个模型只是近似值?
Solution: Laura drives at 10 meters per second for the first second. That means she covers 10 meters in that time. For the second interval, she drives 20 meters per second for 1 second. That gives her 20 more meters of distance, for a cumulative total of 30 meters. And so on, as shown in the table below:
::解答:劳拉驾驶时每秒每秒10米。 这意味着她当时的驾驶时间为10米。 在第二个间隔期间,她驾驶每秒20米,每秒1秒20米。这给了她20多米的距离,累计总长度为30米。 如下表所示:间距(m/s)d(m)0_1010101}t < 22003032}t<3306003}t < 4401004}t < 5501505}t<6602106}t<77028007}t<8803608}t<9904509}t<101005}。
:m/s)d(m)0}t < 110101101}t < 2200302}t<3306003}t < 4401004}t < 4401004}t < 5501505}t < 5501505}t < 660210106}t < 77010606}t < 77028007}t < 88036008}t < 99045009}t < 1000550
Laura's car travels faster each second than the one before
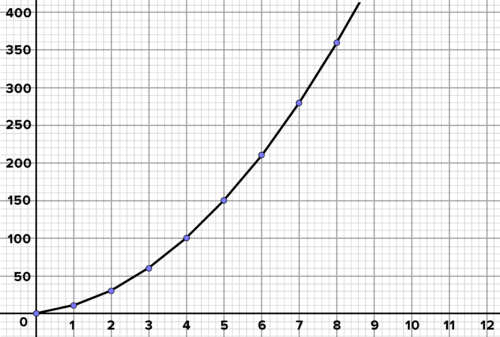
::劳拉的车每秒比前一秒跑快The slope of each interval represents Laura's speed during that interval. The table and graph show that the distance increases by an increasing amount as the intervals advance. The cumulative distance increases by 20, then by 30, then by 40, and so on. This model is only an approximation because it is not possible for her to travel 10 meters per second for the first second, then instantly change her speed to 20 meters per second for the next second. In reality, acceleration is a smooth process of increasing the velocity in every instant. You can say that acceleration is not discrete , that is, it's not broken up as the graph shows. Instead, acceleration is continuous . From the table and graph, you can see that Laura passes the 335-meter mark at about 7.7 seconds.
::每个间距的斜坡代表着劳拉在间隔期间的速度。 表格和图表显示, 距离会随着间隔的推移而增加。 累积距离会增加20, 然后30, 然后40, 等等。 这个模型只是一个近似值, 因为她不可能在第一秒每秒行走10米, 然后立即将速度改变为第二秒每秒20米。 实际上, 加速是一个增加每秒速度的顺利过程。 您可以说加速不是离散的, 也就是说, 它不会像图表显示的那样断裂。 相反, 加速是连续的。 从表格和图表中, 您可以看到劳拉在大约7.7秒时通过335米的标记。The slope of each interval represents Laura's speed during that interval Interactive
::交互式互动How can the model used in the example above be improved? Use the interactive below to experiment with different interval lengths. Consider and discuss the resulting changes in the precision of the model.
::如何改进上述例子中所使用的模型? 使用下面的交互式模型来试验不同的间距长度。 审议和讨论模型精确度因此发生的变化。+Do you want to reset the PLIX?Work It Out
::F. 工 作 外 外-
Suppose Laura acquires a new car that accelerates at 6 meters per second, per second. Complete a table and graph for a piecewise function which models her distance as a function of time. Use an interval length above 1 second. How does this change your model? Estimate the time needed for Laura to complete the 335-meter section.
::假设劳拉购置了一辆每秒6米加速6米的新车。 完成一张表格和图表, 以一个小块函数来模拟距离作为时间函数。 使用超过1秒的间隔长度。 这如何改变您的模型? 估计劳拉完成335米段所需的时间 。 -
Suppose that Laura acquires a racer that accelerates at 8 meters per second, per second. Create a table and graph for two piecewise functions - one with an interval length of 5 seconds, and one with an interval length of 10 seconds. Compare and contrast these models. Use each to estimate when she would complete the 335-meters. Which do you think is more precise and why?
::假设劳拉获得的赛车速度以每秒8米的速度加速, 每秒每秒8米的速度加速。 为两个片段函数创建一个表格和图表, 一个为5秒的间隔长度, 一个为10秒的间隔长度。 比较和对比这些模型。 使用每个模型来估计她何时完成335米。 你认为哪个更精确, 为什么更精确?
::活动2:建立赤道模型In reality, if Laura's acceleration is 10 meters per second, per second, her velocity increases smoothly from 0 meters per second to 10 meters per second in the first second, and so on as she continues to accelerate. Our piecewise function is instructive, but we can improve on it to create a function that tells us the exact distance Laura has traveled at any time. Instead of assuming that she travels 10 meters per second for the entire 1st second, 20 meters per second for the entire 2nd second, and so on, use the average velocity .
::在现实中,如果劳拉的加速度是每秒10米,每秒10米,那么她的速度会从每秒0米顺利上升至每秒10米,然后在她继续加速的时候,等等。我们的片段功能很有启发性,但是我们可以改进它来创造一个函数,告诉我们劳拉在任何时间所走过的确切距离。而不是假设她整个一秒每秒10米,整个二秒每秒20米,等等,使用平均速度。Speedometers measure the velocity of a car Example 2-1
::例2-1Suppose Laura accelerates at 10 meters per second, per second. She does this for 10 seconds. What's her final velocity? What was her initial velocity at 0 seconds? So what is her average velocity over the 10-second time period? Use this to compute the distance Laura has traveled in 10 seconds.
::假设劳拉每秒加速10米,每秒加速10秒。 她这样做了10秒。 她最后的速度是多少? 她的最初速度是多少? 0秒? 她的最初速度是多少? 10秒的平均速度是多少? 用这个来计算劳拉在10秒内行走的距离。Solution:
::解决方案 :-
Laura's final velocity is 100 meters per second.
::劳拉最后的速度是每秒100米 -
Her average velocity is
.
::她的平均速度是100+02=50米/秒。 -
Her distance traveled for 10 seconds at the average velocity of 50 meters per second is
.
::她的距离为10秒,平均速度为每秒50米50-10=500米。 -
This is a perfectly precise value. Because Laura's acceleration was constant, you can average her initial and final velocities to get an average velocity that would give her the equivalent distance.
::这是一个非常精确的值。因为劳拉的加速度是恒定的, 你可以平均她的初始速度和最终速度, 以获得平均速度, 从而获得相等的距离。
Example 2-2
::例2-2Given an acceleration of 10 meters per second, per second, and a time of 3 seconds, compute Laura's distance traveled. Given an acceleration of 8 meters per second, per second, and a time of 12 seconds, compute Laura's distance traveled. Given an acceleration of meters per second, per second, and a time of seconds, write an equation for Laura's distance traveled as a function of time. How is the final velocity computed? Assuming that the initial velocity is always zero, how did you compute the distance traveled?
::如果加速度为每秒10米,每秒3秒,计算劳拉的距离。如果加速度为每秒8米,每秒12秒,计算劳拉的距离。如果加速度为每秒10米,每秒10米,每秒3秒,计算劳拉的距离。如果加速度为每秒8米,每秒12秒,计算劳拉的距离。如果加速度为每秒1米,每秒1秒,每秒2秒1秒,写出劳拉距离的方程式,则根据时间的函数来计算。最后的速度是如何计算出来的?假设最初的速度总是零,你如何计算出所走的距离?Solution: If the acceleration is 10 meters per second, per second and the time is 3 seconds:
::解决方案:如果加速度每秒10米,每秒10米,时间为3秒:-
The final velocity is 30 meters per second.
::最后的速度是每秒30米 -
The initial velocity is 0 meters per second.
::初始速度为每秒0米。 -
So the average velocity is 15 meters per second.
::平均速度是每秒15米 -
That means
.
::d=15(3)=45米。
If the acceleration is 8 meters per second, per second and the time is 12 seconds:
::如果加速度每秒8米,每秒8米,时间为12秒:-
::vfinal=812=96毫秒/秒 -
::vlip=0 m/ 秒 -
::v平均=962=48米/秒 -
::d=48=12=576米
In general, the final velocity is computed by multiplying the acceleration by the time:
::一般而言,最后速度的计算方法是将加速度乘以下列时间:You compute the average velocity by averaging the initial velocity and final velocity:
::您通过平均初始速度和最终速度来计算平均速度 :
::v平均= v Final+vstim2But since the initial velocity in this scenario is always 0, the average velocity is just the final velocity divided by 2:
::但既然最初的速度 总是0, 平均速度只是最后的速度 以2除以2。
::v平均=v final2Remember, the final velocity is just acceleration times time, so:
::记住,最后的速度只是加速时间,所以:
::v平均=at2And to compute the distance, you multiply the average velocity times the time:
::要计算距离,您要乘以平均速度乘以时间的倍数:
::d= at2t
::d= at22
::d=12at2The Quadratic Model for an Object with Constant Acceleration
::恒常加速对象的二次曲线模型If an object has a constant acceleration , the distance the object has traveled after time is given by the equation .Work it Out
::工作出来-
If Laura's car accelerates at 10 meters per second, per second, create the equation for her distance as a function of time. Graph the function. Use the graph to approximate when she passes the 335-meter mark.
::如果劳拉的车加速到每秒10米,每秒10米, 将她的距离作为时间函数来创建方程式。 绘制函数。 使用图表来估计她通过335米标记时的距离 。 -
Write and solve an equation to answer the last question. Use the following example to solve that equation.
::写入并解析一个方程式以解答最后一个问题。 使用以下示例解答此方程式 。
How to solve a simple quadratic equation for positive solutions
::如何解决积极解决方案的简单二次方程式Example quadratic equation solution:
-
Identify each of the following functions as quadratic, linear, exponential, or none of those. Explain your decisions. For each, describe how the parameters of the equation affect the table and graph.
-
::y=7x2 y=7x2 -
::y=5x+17 y=5x+17 -
::y=3(2)x -
::y=x3 y=x3 -
::y2=x2+3 y2=x2+3 -
::y=12( 23) x -
::y=0.3x2 y=0.3x2
::将以下函数中的每一个函数标记为二次函数、线性函数、指数函数或无函数。 请解释您的决定。 对于每一个函数, 请描述方程参数如何影响表格和图形。 y= 7x2 y= 5x+17 y= 3(2)x y= 3(2)x y= 3 y= 3 y= y2=x2+3 y= 12( 23x y=0. 3x2) -
-
What is the basic structure of a quadratic function? What distinguishes a quadratic function from a
linear function
or an
exponential function
?
::二次函数的基本结构是什么?二次函数与线性函数或指数函数有何区别? -
(extension) If Laura's car accelerates at 20 meters per second per second, create the equation for her distance as a function of time. Create a table which shows the values returned for
integers
from 0 to 10. Subtract consecutive
-values. Look for patterns and describe your observations.
::如果劳拉的汽车加速速度为每秒20米/秒, 则根据时间函数为其距离创建方程式。 创建一个表格, 显示从 0 到 10 的整数返回的数值 。 将连续的 y 值减为 y 值 。 查找图案并描述您的观察结果 。 -
(extension) So far you've explored three different function types. What are they? What are the differences and similarities between their tables, equations, and graphs? Give examples of scenarios that are best modeled by each type.
::到目前为止,您已经探索了三种不同的函数类型。 它们是什么? 它们的表格、 方程和图表之间有什么不同和相似之处? 请举例说明每种类型最能模拟的情景。
Piecewise, Linear, and Quadratic Graph Types Summary
::摘要-
Piecewise functions can help explore and build a continuous function.
::小数函数可以帮助探索和构建一个连续函数。 -
Quadratic functions feature a squared term and can be used to model scenarios involving objects experiencing constant acceleration.
::二次曲线函数有一个方形词,可用于模拟不断加速的物体的假设情况。 -
Linear equations do not have variables with powers greater than one.
::线性方程式没有功率大于一个的变量。
-
Complete the table with her total completed distance at the end of each interval.