2.9细胞转运
章节大纲
-
How is a like a castle wall?
::城堡墙怎么样?The walls of a castle, like the cell membrane, are designed to keep out dangerous things. Whether you're concerned about an enemy army or a disease-causing bacteria , you don't want to allow everything to enter! However, to survive, there are some things that the cell (or the castle) does need to let in.
::城堡的墙壁,就像细胞膜一样,是设计来防止危险事物的。不管你关心的是敌军还是疾病细菌,你都不想让一切进入。然而,为了生存,细胞(或城堡)确实需要让某些东西进入。Introduction to Cell Transport
::单元格运输介绍Cells are found in all different types of environments, and these environments are constantly changing. For example, one-celled organisms , like bacteria, can be found on your skin, in the ground, or in all different types of water. Therefore, cells need a way to protect themselves. This job is done by the cell membrane, which is also known as the plasma membrane.
::细胞存在于所有不同类型的环境中,这些环境在不断变化。例如,单细胞生物,如细菌,可以在你的皮肤、地面或各种水中找到。因此,细胞需要一种保护自己的方式。这项工作由细胞膜完成,也被称为等离子膜。Controlling the Cell Contents
::控制单元格内容The cell membrane is semipermeable , or selectively permeable , which means that only some molecules can pass through the membrane. If the cell membrane were completely permeable, the inside of the cell would be the same as the outside of the cell. It would be impossible for the cell to maintain . Homeostasis means maintaining a stable internal environment. For example, if your body cells have a temperature of 98.6°F, and it is freezing outside, your cells will maintain homeostasis if the temperature of the cells stays the same and does not drop with the outside temperature.
::细胞膜是半渗透的,或者有选择地渗透到细胞膜中,这意味着只有某些分子才能通过细胞膜。如果细胞膜完全可以渗透到细胞膜中,细胞的内部与细胞外部是相同的。细胞内部将无法维持。软骨保持意味着保持稳定的内部环境。例如,如果身体细胞的温度为98.6°F,并且外面是冷冻的,那么如果细胞的温度保持不变,并且不随外部温度下降,细胞的内脏将保持恒定状态。How does the cell ensure it is semipermeable? How does the cell control what molecules enter and leave the cell? The composition of the cell membrane helps to control what can pass through it.
::单元格如何确保它是半渗透的? 细胞如何控制分子进入和离开细胞? 细胞膜的构成有助于控制能够穿过它的东西。Composition of the Cell Membrane
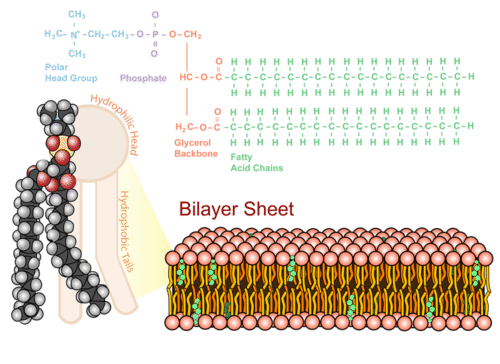
::细胞膜构成Molecules in the cell membrane allow it to be semipermeable. The membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids (a "bilayer") and proteins ( Figure ). Recall that phospholipids, being lipids , do not mix with water. It is this quality that allows them to form the outside barrier of the cell.
::细胞膜中的分子允许其半渗透性。 膜是由一层双层的磷素(“ 双层 ”) 和蛋白质( 图表 ) 制成的。 请注意, 磷素是脂质, 不与水混合。 正是由于这种质量, 才能形成细胞的外部屏障 。A single phospholipid molecule has two parts:
::单一种磷素分子有两个部分:- A polar head that is hydrophilic , or water-loving.
::极地头有水利病,或爱水。
- A fatty acid tail that is hydrophobic , or water-fearing.
::脂肪酸尾巴是疏水或防水的。
The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer, two layers of phospholipid molecules. Notice the polar head group of the phospholipid is attached to the phosphate, and the tails are two fatty acid chains. The head group and tails are attached by a glycerol backbone. There is water found on both the inside and the outside of cells. Since hydrophilic means water-loving, and they want to be near water, the heads face the inside and outside of the cell where water is found. The water-fearing, hydrophobic tails face each other in the middle of the cell membrane, because water is not found in this space. The phospholipid bilayer allows the cell to stay intact in a water-based environment.
::细胞内外都发现了水,因为水利生物是指爱水,它们想靠近水,所以头部面对发现水的细胞内外。防水、防水的尾巴在细胞膜中间相互对峙,因为在这个空间里找不到水。磷素双层使细胞能够在水基环境中保持完整。An interesting quality of the plasma membrane is that it is very "fluid" and constantly moving, like a soap bubble. This fluid nature of the membrane is important in maintaining homeostasis. It allows the proteins in the membrane to float to areas where they are needed.
::等离子膜的一个有趣的质量是,它非常“流体 ” , 并且像肥皂泡一样不断移动。 膜的这种流体性对于保持均匀状态很重要。 它允许膜中的蛋白质漂浮到需要它们的地方。Due to the composition of the cell membrane, small molecules such as oxygen and carbon dioxide can pass freely through the membrane, but other molecules, especially large molecules, cannot easily pass through the plasma membrane. These molecules need assistance to get across the membrane. That assistance will come in the form of transport proteins .
::由于细胞膜的构成,氧和二氧化碳等小分子可以自由通过膜,但其他分子,特别是大分子,不能轻易通过等离子膜。这些分子需要帮助才能穿过膜。援助的形式是迁移蛋白质。Summary
::摘要- The cell membrane is selectively permeable, meaning only some molecules can get through.
::细胞膜有选择性地渗透,意味着只有某些分子能穿透。
- The cell membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids, each with a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-fearing) tail.
::细胞膜由一层双层磷素制成,每层都有一种(爱水的)水益头和防水(敬畏水的)尾部。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resources below to answer the following questions.
::利用以下资源回答下列问题。I) Active and Passive Transport at (6:13)
:一) 主动和被动运输(6:13)
- How is passive transport different from active transport?
::被动运输与主动运输有何不同?
- What are three types of passive transport? What do these all have in common?
::什么是三种类型的被动运输?这些都有哪些共同点?
- What does the body use iodine for? What kind of transport is necessary to transport this molecule into a cell?
::人体使用碘做什么?
- What happens to the receptor complex in receptor mediated endocytosis?
::受体介于内分泌硬化的受体综合体会怎样?
Review
::回顾- Why is the plasma membrane considered selectively permeable? Why is this important?
::为什么等离子膜被认为是选择性渗透的?为什么这很重要?
- Explain the composition of the cell membrane.
::解释细胞膜的构成。
- Explain the arrangement of phospholipids in the membrane.
::解释一下脑膜中磷素的安排。
- A polar head that is hydrophilic , or water-loving.