答复 - Ch 2:函数和图表
章节大纲
-
Section 2.2: Domain and Range
::第2.2节:面积和范围-
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
[
-
1
,
1
]
::域 : x (- , ) 范围 : y [-1, 1] -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
2
)
∪
[
3
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
[
-
8
,
∞
)
::域 : x -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
[
0
,
2
]
::域 : x (- , ) 范围 : y [0, 2] -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
[
-
3
,
∞
)
::域 : x (- , ) 范围 : y [-3, ] -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
∞
,
2
]
::域 : x (- , ) 范围 : y (- , 2) -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
1
,
∞
)
::域 : x (- , ) 范围 : y (-1, ) -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
3
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
::域 : x (3, ) 域 : y (- , ) -
Domain:
x
∈
{
-
2
,
3
4
,
π
2
,
2
,
3
}
Range:
y
∈
{
1
,
π
,
5
,
7
}
::域 : x { { 2, 34, 2, 2, 3} 范围 : y { { 1, , 5,7} -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
∞
,
4
]
::域 域 : x (- , ) 域 : y (- , ) 4 -
Domain:
x
∈
(
1
2
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
::域 : x (12, ) 范围 : y (-, , ) -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
1
)
∪
(
1
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
∞
,
0
)
∪
(
0
,
∞
)
::域 : x (- , 1, ) (1, ) 范围 : y (- , 0) (0, ) 。 -
Domain:
x
∈
[
-
4
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
∞
,
-
1
]
::域 : x [ 4 ] 范围 : y (- , -1) -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
-
6
)
∪
(
-
6
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
∞
,
-
1
)
∪
(
-
1
,
∞
)
::域 : x (- , , , , , , , , , ) 范围 : y (- , , , , , , , , , ) 范围 : y (- , , , , , ) -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
-
1
)
∪
(
1
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
::域 : x (- ,-1, ) 域 : y (- , ) -
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
-
1.5
]
∪
[
1.5
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
[
6
,
∞
)
::域 : x (- ,- 1.5] [1.5, ] 范围 : y [6, ] -
The independent variable is
h
, the hours he worked. Domain:
x
∈
[
20
,
25
]
Range:
y
∈
[
200
,
250
]
::独立的变量是h, 他工作的时间。 域 : x [ 20, 25] 范围 : y [ 200, 250] -
Domain:
x
∈
[
10
,
12
]
Range:
y
∈
[
300
,
360
]
She can drive between 300 and 360 miles.
::域 : x [10,12] 范围 : y [300,360] 她可以驾驶300至360英里。 -
Domain:
x
∈
[
4
,
8
]
Range:
y
∈
[
11
,
22
]
The evening cost between $11 and $22.
::域: x [4,8] 范围: y [11,22] 晚间费用在11美元至22美元之间。
Section 2.3: Maximums and Minimums
::第2.3节:最高和最低-
There is a global minimum at (3, 0).
::全球最低值(3 0)为全球最低值。 -
There
is a local minimum at (3, 0).
::当地最低限额为3 0。 -
Global minimum at
(
-
π
2
,
-
1
)
,
and global maximum at
(
π
2
,
1
)
::全球最低值(-__2,-1),全球最高值(-2,-1),全球最高值(-2,1) -
Local minimum at
(
-
π
2
,
-
1
)
,
and local maximum at
(
π
2
,
1
)
::当地最低值(-%2,-1),当地最高值(-%2,-1),当地最高值(-%2,1) -
There are no global extrema.
::没有全球极端现象。 -
There are no local extrema.
::当地没有直径。 -
There are no global extrema.
::没有全球极端现象。 -
Local minimums: (0.4, -1), (2.5, -13). Local maximums: (-1.5, 22), (1, 0). [Note: Points are approximate.]
::当地最低数值0.4)-1,(2.5,-13),当地最高数值
-1.5,22),(1,0),[注:要点大致相同。 ]
-
There are no global extrema.
::没有全球极端现象。 -
Local minimum: (3, 0). Local maximum: (0.5, 9.5). [Note: Points are approximate.]
::当地最低比率3 0) 当地最高比率
0.5,9.5) [注:要点大致相同。 ]
-
A global maximum is the overall highest point on the graph, while the local maximum is the highest point within a certain neighborhood of the graph.
::全球最大值是图中的总最高点,而本地最高值是图中某个区域的最高点。 -
Answers vary. Graph should show a global minimum, a local maximum, and no global maximum. (There can be a local minimum.)
::答案各有不同。图表应显示全球最低值、地方最高值、全球最高值。 (当地最低值可以是当地最低值。 ) -
Answers vary. Graph should have no global extrema, but both types of local extrema.
::答案各有不同。图中不应有全球性的外形,但两种类型的局部外形。 -
Local maximum: (-1.16, 36.24). Local minimum: (-4, 0). No global maximum. Global minimum: (2,16, -18.49).
::当地最高额-1.16, 36.24) 当地最低额
4, 0) 全球最高额; 全球最低额
2,16, 18.49)。
-
Local maximum: (-1,0). Local minimum: (0.22, -3.23). Global maximum: (2.28, 9.91). No global minimum.
::当地最高值-1,0)当地最低值
0.22,-3.23)全球最高值
2.28,9.91)没有全球最低值。
-
A length and width of approximately 4.472 will minimize the perimeter. The perimeter would be approximately 17.889 inches.
::长度和宽度约为4.472,将最大限度地缩小周界,周界约为17.889英寸。 -
A
=
w
⋅
(
P
−
2
w
2
)
or
A
=
-
w
2
+
1
2
P
w
.
The rectangle with the maximum area would be the one where the width is 1/4 of the perimeter.
::A=w(P- 2w2) 或 A=-w2+12Pw。 最大面积的矩形将是宽度为周界四分之一的矩形。 -
800 square feet
::800平方英尺
Section 2.4: Symmetry
::第2.4节:对称-
Even
::偶偶偶 -
Odd
::奇数 -
Neither
::中 无 -
Neither
::中 无 -
Odd
::奇数 -
Neither
::中 无 -
Neither
::中 无 -
Even
::偶偶偶 -
f
(
-
x
)
=
h
(
-
x
)
−
g
(
-
x
)
=
h
(
x
)
+
g
(
x
)
≠
f
(
x
)
o
r
-
f
(
x
)
:f-x) =h(-x) -g(-x) =h(x) +g(x) +g(x) f(x) 或-f(x)
-
f
(
-
x
)
=
h
(
-
x
)
g
(
-
x
)
=
-
h
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
=
-
f
(
x
)
:f-x)=h(x)g(x)=-h(x)g(x)=-h(x)g(x)g(x)=-f(x)
-
f
(
-
x
)
=
h
(
-
x
)
g
(
-
x
)
=
-
h
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
=
-
f
(
x
)
:f-x)=h(x)g(x)=-h(x)g(x)=-h(x)g(x)g(x)=-f(x)
-
Yes. If
h
(
x
)
and
g
(
x
)
are both even and
f
(
x
)
=
h
(
x
)
+
g
(
x
)
, then
f
(
−
x
)
=
h
(
−
x
)
+
g
(
−
x
)
=
h
(
x
)
+
g
(
x
)
=
f
(
x
)
.
::是。如果 h(x) 和 g(x) 是偶数 和 f(x) = h(x)+g(x),那么 f(x) = h(x) = h(x) +g(x) = h(x) = h(x)+g(x) = h(x)+g(x)= f(x)。 -
Yes. If
h
(
x
)
and
g
(
x
)
are both odd and
f
(
x
)
=
h
(
x
)
+
g
(
x
)
, then
f
(
−
x
)
=
h
(
−
x
)
+
g
(
−
x
)
=
−
h
(
x
)
−
g
(
x
)
=
−
[
h
(
x
)
+
g
(
x
)
]
=
−
f
(
x
)
::是 。 如果 h( x) 和 g( x) 既为奇数, 且 f( x) = h( x) +g( x) , 那么 f( x) = h( x) = h( x) +g( - x) +g( x) - x) \ (x) \ (x) \ [h( x) +g( x)]\ f( x) -
There are some functions that do not have reflection symmetry across the
y
-axis, or rotation symmetry about the origin.
::有一些函数在 Y 轴之间没有反射对称,或者对原值没有旋转对称。 -
If a function is even, then it is symmetrical across the
y
-axis. If a function is odd, then it has rotation symmetry about the origin.
::如果函数是偶数,则在 Y 轴之间对称。如果函数是奇数,则会对原值进行旋转对称。
Section 2.5: Increasing and Decreasing
::第2.5节:增加和减少-
Increasing:
x
∈ (3,
∞
)
::增加: x (3, ) -
Decreasing:
x
∈ (
-
∞
,3)
::下降: x (- , 3) -
Increasing:
x
∈ (
-
π
2
,
π
2
)
::增加: x (- 2, 2) -
Decreasing:
x
∈ (
-
π
,
π
2
) ∪ (
π
2
,
π
)
::下降: x (- , 2) ( 2, ) -
Increasing:
x
∈ (
-
∞
,
∞
)
::增加: x (- , ) -
None
::无无无无无无无 -
Increasing:
x
∈ (
-
∞
, -1.4) ∪ (0.3, 1) ∪ (2.5,
∞
) [Note: Points are approximate.]
::增加: x (- , - 1.4) (0.3, 1) (2.5, ) [注:要点大致相同。 ] -
Decreasing:
x
∈ (-1.4, 0.3) ∪ (1, 2.5) [Note:
P
oints are approximate.]
::下降: x (1.4, 0.3) (1, 2.5) [注:要点大致相同。 ] -
Increasing:
x
∈ (-
∞
, 0.3) ∪ (3,
∞
)
::增加: x (- , 0. 3) (3, ) -
Decreasing:
x
∈ (0.3, 3)
::下降: x (0.3, 3) -
Answers vary. [Possible answer: A line with a positive slope.]
::[可能的答案:正斜坡线。 ] -
Answers vary. [Possible answer: A line with a negative slope.]
::[可能的答案:负斜度线。 ] -
Increasing:
x
∈ (-
∞
, 1) ∪ (3,
∞
) & Decreasing:
x
∈ (1, 3)
::递增: x (- , 1) (3, ) 和 递减: x (1, 3) -
Increasing:
x
∈ (-
∞
, 1) & Decreasing:
x
∈ (1,
∞
)
::递增: x (- , 1) 和 递减: x (1, ) (1, ) -
Increasing:
x
∈ (5,
∞
) & Decreasing:
x
∈ (-
∞
, 5)
::增加: x (5, ) 和 减少: x (- , 5) -
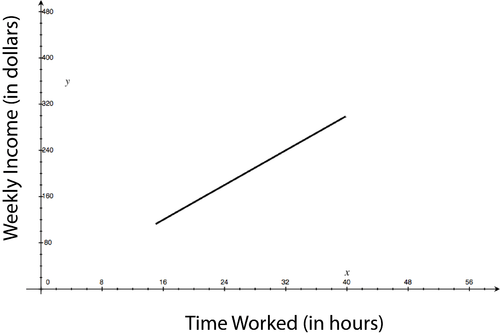
Extrema are at (15, 112.5) and (40, 300).
::异常值为(15,112.5)和(40,300)。 -
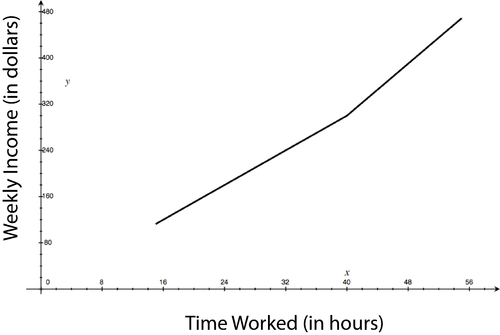
Max value changes if he works overtime. The new extrema are (15, 112.5) and (55, 468.75).
::如果他加班,最大值会变化。新的外形是(15,112.5)和(55,468.75)。 -
Extrema are (15, 112.5) and (55, 468.75).
::异端是(15,112.5)和(55,468.75)。
Section 2.6: Intercepts of Graphs of Functions
::第2.6节:职能图图的截断-
y
-intercept: (0, -4); Zeroes: (-1,0) and (4, 0)
::y 拦截: (0, - 4); 零1,0)和(4,0)
-
y
-intercept: (0, -12); Roots: (-3,0), (1,0), and (2, 0)
::y 拦截: (0, - 12); 根30,0, 1,0) 和(2, 0)
-
y
-intercept is approximately (0, 6),
x
-intercepts are (-2,0) and (1, 0)
::y 拦截大约为( 0, 6), x 拦截是( 2, 0) 和(1, 0) -
Both
x
- and
y
-
intercepts are at (0,0).
::X 和 y 的界面都在 0,0 。 -
Both
x
- and
y
-intercepts are at (0,0).
::X 和 y 的界面都在 0,0 。 -
No
y
-intercept;
x
-intercept is (1, 0).
::没有 y 界面; x 界面是 1, 0 。 -
No
x
- or
y
-intercepts
::无 x 或 Y 界面 -
y
-intercept is (0, 1); no
x
-intercept
::y 界面是 (0, 1); 没有 x 界面 -
Both
x
- and
y
-intercepts are (0,0).
::X 和 y 界面为 0,0 。 -
Yes, because there are functions that are undefined when
x
=
0
.
::是, 因为有函数在 x=0 时未定义 。 -
Yes, because there are functions with no real solutions when
y
=
0
.
::是的, 因为有函数在 y=0 时没有真正的解决方案 。 -
The
x
-intercept of
f
(
x
)
is called a zero because it is the solution to
f
(
x
)
=
0
.
::f( x) 的 x interview 被称为 0 , 因为它是 f( x) = 0 的解决方案 。 -
y
-intercept: (0, 10);
x
-intercepts: (2,0), (-1,0), (5,0)
::y 拦截: (0, 10); x 拦截: (2,0), (1,0), (5,0) -
y
-intercept: (0, -7);
x
-intercepts: (-1,0), (7,0)
::y 拦截0, - 7); x 拦截
1,0),(7,0)
-
y
-intercept: (0, 5);
x
-intercepts: (5,0), (-1/2, 0), (1,0)
::y 拦截: (0, 5); x 拦截: (5,0), (1, 2, 0), (1,0)
Section 2.7: Function Families
::第2.7节:功能家庭-
y
=
b
x

::y=bx y=bx -
y
=
log
b
x

::y=logbx y=logbx y=logbx logbx y=logbx logbx y=logbx y=logbx logbx y=logbx y=logbx y=logbx logbx y=logbx y=logbx y=logbx y=logbx -
y
=
sin
x

::y=sinx y=sinx y=sinx y=sinx y=inx y=sinx y=sinx y=sinx y=sinx y=sinx y=sinx y=sinx -
y
=
x
2

::y=x2 y=x2 -
y
=
|
x
|

::~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ -
y
=
1
x

::y=1x y=1x -
y
=
1
1
+
b
-
x

::y=11+b-x y=11+b-x -
y
=
√
x

::yx -
y
=
x
3

::y=x3 y=x3 -
y
=
x

::y=x y=x -
y
=
1
x
because
1
0
is undefined.
::y=1x 因为 10 未定义 。 -
y
=
e
x
,
y
=
x
2
,
y
=
√
x
,
y
=
|
x
|
::y=ex,y=x2,y=x,y=xx,y=xx -
One difference is
y
=
x
2
has a minimum value, while
y
=
x
3
doesn't.
::一个差异是 Y=x2 有最小值, 而 y=x3 没有 。 -
The two graphs are reflections of one another across the line
y
=
x
.
::这两个图表是横跨y=x线的相互反射。 -
y
=
√
x
is not defined for all values of
x
because the square root of any negative number is not a real number.
::yx 没有定义 x 的所有值, 因为任何负数的平方根不是实际数字 。
Section 2.8: Graphical Transformations
::第2.8节:图形转换-
Reflection across the
x
-axis and reflection across the
y
-axis.
::反射到X轴 反射到Y轴 反射到Y轴 -
Reflection across the
x
-axis and a horizontal shift left 3 units.
::X轴反射和横向移动左倾3个单位。 -
Horizontal shift left 1 unit and vertical shift down 2 units.
::水平向左移动 1 个单位,垂直向下移动 2 个单位。 -
Reflection across the
y
-axis and horizontal shift right 3 units.
::反射到Y轴和水平向右3个单位 -
Reflection across the
x
-axis and horizontal compression by a factor of 2.
::反射 X 轴和水平压缩的乘数为 2。 -
Vertical stretch by a factor of 4, horizontal stretch by a factor of 2, and horizontal shift left 2 units.
::垂直伸展以4为因数,水平伸展以2为因数,水平移移以2为因数,水平移移以2为单位。 -
A reflection across the
x
-axis, a horizontal shift right 2 units, vertical shift down 2 units, and a vertical stretch by a factor of 3.
::X轴反射, 水平向向右移 2 个单位, 垂直向下移 2 个单位, 垂直伸展 3 倍 。 -
Vertical stretch by a factor of 5 and a horizontal shift left 1 unit.
::垂直伸展以5为因数,水平向向向左倾移1个单位。 -
2
h
(
x
−
2
)
+
3
::2h(x-2)+3 -
-
f
(
x
+
2
)
−
1
::-f(x+2)-2-1 -
1
4
g
(
−
x
)
::14g(-x) 14g(-x) -
3
j
(
x
−
2
)
+
3
::3j(x-2)+3 -
k
(
1
4
(
x
+
1
)
)
+
3
::k14( x+1) +3 -
::12h(-(x-3))) -
-
5
f
(
x
)
::-5f(x)
Section 2.9: Transforming Functions Defined by Data
::第2.9节:数据界定的转换功能-
Vertical reflection across the
x
-axis, vertical compression by a factor of 2, horizontal shift 1 unit left.
( x , y ) → ( x − 1 , − y 2 )
x y 0 5 1 6 2 7 → x y - 1 - 5 2 0 - 6 2 1 - 7 2
::X轴垂直反射,垂直压缩乘以 2, 水平倾角 1 单位左转。 (x,y) (x-1,-y2) xy051627 Xy-1-520-621-72 -
Vertical stretch by a factor of 2, horizontal compression by a factor of 3, and vertical shift up 2 units.
( x , y ) → ( x 3 , 2 y + 2 )
x y 0 5 1 6 2 7 → x y 0 12 1 3 14 2 3 16
::垂直伸展乘以 2, 垂直伸展乘以 2, 水平压缩乘以 3, 垂直向上移动 2 个单位 。 (x,y) (x3, 2y+2) (x3, 2y+2) × 051627 xy012113142316) -
Reflection across the
x
-axis, horizontal shift 4 units to the right, vertical shift 3 units down.
( x , y ) → ( x + 4 , − y − 3 )
x y 0 5 1 6 2 7 → x y 4 - 8 5 - 9 6 - 10
::反射 x 轴, 水平向向右倾移 4 个单位, 垂直向下移 3 个单位 。 (x, y) (x+4, - y- 3) xy051627 xy4- 85- 96- 10 -
Vertical stretch by a factor of 3, horizontal compression by a factor of 2, horizontal shift 2 units to the right, and vertical shift up 1 unit.
( x , y ) → ( x 2 + 2 , 3 y + 1 )
x y 0 5 1 6 2 7 → x y 2 16 2 1 2 19 3 22
::垂直伸展 3 乘以 3, 垂直伸展 3, 水平压缩 以 2 乘以 2 , 向右水平倾斜 2 个单位, 向上垂直向上移 1 个单位 。 (x,y) (x2+2, 3y+1, xy+1) xy051627 xy21621219322 -
Reflection across the
x
-axis, horizontal shift right 3 units.
( x , y ) → ( x + 3 , - y )
x y 0 5 1 6 2 7 → x y 3 - 5 4 - 6 5 - 7
::X轴反射, 水平向向向右3 个单位。 (x,y) (x+3,-y) xy051627 xy3-54- 65-7 -
f
(
x
)
→
f
(
2
x
−
6
)
−
4
:xx) f(2x-6)-4
-
f
(
x
)
→
−
f
(
x
2
−
2
)
+
1
:xx)-(x2-2)+1
-
f
(
x
)
→
3
f
(
x
4
)
−
5
:xx) 3f(x4)-5
-
f
(
x
)
→
−
f
(
x
2
)
+
1
:xx)-(x2)+1
-
f
(
x
)
→
−
f
(
x
3
)
+
1
:xx)-(x3)+1
-
(
x
,
y
)
→ (
x
+
2
,
3
y
+
1
)
:x,y) (x+2, 3y+1)
-
(
x
,
y
)
→ (
x
+
1
,
-
4
y
+
3
)
:x,y) (x+1,-4y+3)
-
(
x
,
y
)
→ (
x
2
−
1
,
y
2
−
5
)
:x,y) (x2-1,y2-5)
-
(
x
,
y
)
→ (
2
x
+
4
,
5
y
−
1
)
:x,y) (2x+4,5y-1)
-
(
x
,
y
)
→ (
x
2
+
2
,
y
4
)
:x,y) (x2+2, y4)
Section 2.10: Asymptotes and End Behavior
::第2.10节:小粒子和最终行为-
There are no asymptotes. As
x
approaches positive infinity,
y
approaches positive infinity. As
x
approaches negative infinity,
y
approaches negative infinity.
::没有微粒。 x 接近正无穷, y 接近正无穷。 x 接近负无穷, y 接近负无穷。 -
There are no asymptotes. As
x
approaches both positive and negative infinity,
y
approaches positive infinity.
::不存在微粒。 x 既接近正无穷又接近负无穷, y 接近正无穷。 -
There are no asymptotes. As
x
approaches positive infinity,
y
approaches positive infinity. As
x
approaches negative infinity,
y
approaches negative infinity.
::没有微粒。 x 接近正无穷, y 接近正无穷。 x 接近负无穷, y 接近负无穷。 -
There are no asymptotes. As
x
approaches positive infinity,
y
approaches positive infinity.
::没有微量的微量。 x 接近正无穷, y 接近正无穷。 -
There is a horizontal asymptote at
y
=
0
and a vertical asymptote at
x
=
0
. As
x
approaches both positive and negative infinity,
y
approaches 0.
::y=0 有水平的同量点, x=0 有垂直的同量点。 x 接近正和负无穷, y 接近0 。 -
As
x
approaches negative infinity, there is a horizontal asymptote at
y
=
0
. As
x
approaches positive infinity,
y
approaches positive infinity. There is no vertical asymptote.
::x 接近负无限度时, y=0 存在水平零点。 x 接近正无穷度时, y 接近正无穷度时, 没有垂直无穷。 -
There is a vertical asymptote at
x
=
0
. As
x
approaches positive infinity,
y
approaches positive infinity. As
x
approaches 0,
y
approaches negative infinity. There is no horizontal asymptote.
::x=0 时有一个垂直的无线点。 当 x 接近正无线点时, y 接近正无线点。 x 接近 0 时, y 接近负无线点。 没有水平的无线点 。 -
As
x
approaches negative infinity, there is a horizontal asymptote at
y
=
0
. As
x
approaches positive infinity, there is a horizontal asymptote at
y
=
1
. There is no vertical asymptote.
::x 接近负无限度时, y= 0 时会出现水平零星。 x 接近正无穷度时, y= 1. 没有垂直无穷。 -
There is a vertical asymptote at
x
=
0
. As
x
approaches positive infinity, there is a horizontal asymptote at
y
=
0
. As
x
approaches negative infinity, there is a horizontal asymptote at
y
=
2
.
::x=0 时有一个垂直的静态。 x 接近正无穷, y=0 时有一个水平的静态。 x 接近负无穷, y=2 时有一个水平的静态。 -
There is a vertical asymptote at
x
=
1
. As
x
approaches both positive and negative infinity, there is a horizontal asymptote at
y
=
2
.
::x=1. x接近正和负无穷时,y=2是水平的无穷状态。 -
There is a vertical asymptote at
x
=
4
. As
x
approaches both positive and negative infinity, there is a horizontal asymptote at
y
=
1
.
::x=4. x接近正和负无穷时,y=1是水平的无穷状态。 -
Because when
x
=
0
,
y
=
1
0
,
which is undefined.
::因为当 x=0, y=10, 未定义 。 -
Because when
x
=
−
3
,
y
=
1
0
,
which is undefined.
::因为当 x3, y=10, 未定义时 。 -
x
=
2
::x=2x=2 -
x
=
-
4
::x=-4x=-4
Section 2.11: Continuity and Discontinuity
::第2.11节:连续性和中断-
This function is continuous.
::此函数是连续的 。 -
This function is continuous.
::此函数是连续的 。 -
This function is continuous.
::此函数是连续的 。 -
This function is continuous on its domain.
::此函数在其域内是连续的 。 -
Infinite discontinuity at
x
=
0
.
::x=0时无限不连续。 -
This function is continuous.
::此函数是连续的 。 -
This function is continuous on its domain.
::此函数在其域内是连续的 。 -
This function is continuous.
::此函数是连续的 。 -
There is a removable discontinuity at
x
=
-
2
, infinite discontinuity at
x
=
0
, and a jump discontinuity at
x
=
4
.
::x=2时有可移动的不连续状态, x=0时有无限不连续状态, x=4时有跳跃不连续状态。 -
There is a removable discontinuity at
x
=
2
.
::x=2时有可移动的不连续性。 -
There is a jump discontinuity at
x
=
0.3
.
::x=0. 3 时有跳跃不连续状态。 -
Answers vary, but should show
f
(
x
)
has a jump discontinuity at
x
=
3
, a removable discontinuity at
x
=
5
, and another jump discontinuity at
x
=
6
.
::答案各有不同,但应显示 f(x) 在 x=3 时有跳跃不连续性, x=5 时有可移动不连续性,而在 x=6 时又有跳跃不连续性。 -
Answers vary, but should show
g
(
x
)
has a jump discontinuity at
x
=
-
2
, an infinite discontinuity at
x
=
1
, and another jump discontinuity at
x
=
3
.
::答案不尽相同,但如果显示 g(x) 在 x= 2 时跳跃不连续, 在 x= 1 时无限不连续, 在 x= 3 时再次跳跃不连续, 则显示 g(x) 在 x= 3 时跳跃不连续。 -
Answers vary, but should show
h
(
x
)
has a removable discontinuity at
x
=
-
4
, a jump discontinuity at
x
=
1
, and another jump discontinuity at
x
=
7
.
::答案不尽相同,但如果显示 h(x) 在 x= 4 时具有可移动的不连续性, 在 x= 1 时具有跳跃不连续性, 在 x= 7 时则具有另一个跳跃不连续性, 则显示 h(x) 在 x= 7 时具有可移动的不连续性。 -
Answers vary, but should show
j
(
x
)
has an infinite discontinuity at
x
=
0
, a removable discontinuity at
x
=
1
, and a jump discontinuity at
x
=
4
.
::答复各有不同,但应显示j(x)在 x=0 时具有无限不连续性,在 x=1 时具有可移动不连续性,在 x=4 时具有跳跃不连续性。
Section 2.12: Function Combinations and Composition
::第2.12节:职能组合和组成-
g
(
x
)
−
h
(
x
)
=
(
x
−
2
)
2
−
3
−
(
−
x
)
=
x
2
−
3
x
+
1
::g(x)-h(x)=(x)-2,2-3-(x)=x2-3x+1 -
f
(
x
)
=
|
x
|

h ( x ) = - x

g ( x ) = ( x − 2 ) 2 − 3

:xx)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ -\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\
-
f
(
g
(
x
)
)
=
|
(
x
−
2
)
2
−
3
|
=
|
x
2
−
4
x
+
1
|
:g(xx)) (x-2) 2 - 3x2 - 4x+1
-
The absolute value from
f
(
x
)
made all negative
y
values for
g
(
x
)
positive.

::f( x) 的绝对值使 g( x) 的所有负值为正值。 -
g
(
f
(
x
)
)
=
(
|
x
|
−
2
)
2
−
3
::g(f(x)) = (x%2) 2- 3 -
Since the absolute value function is even, it created a similar reflection in
g
(
x
)
.

::由于绝对值函数是偶数,它在 g(x) 中产生了类似的反射。 -
h
(
g
(
x
)
)
=
-
[
(
x
−
2
)
2
−
3
]
=
-
(
x
−
2
)
2
+
3
::h(g(xx))=-[(x-2)2-2-3]=-(x-2)2+3 -
The negative from
h
(
x
)
reflects
g
(
x
)
across the
x
-axis.

::h( x) 的负数反映 X 轴横跨的 g( x) 。 -
g
(
h
(
x
)
)
=
x
2
+
4
x
+
1
::g( h(x)) =x2+4x+1 -
The negative from
h
(
x
)
reflects
g
(
x
)
across the
y
-axis.

::h( x) 的负数反映 Y 轴对面的 g( x) 。 -
j
(
x
)
+
m
(
x
)
=
x
2
+
√
x
::j(x)+m(x)=x2=x2}x -
j
(
x
)
=
x
2

k ( x ) = | x |

m ( x ) = √ x

::j(x) =x2 k(x) m(x) x -
j
(
k
(
x
)
)
=
|
x
|
2
::jj(k(x)) x2 -
Since squaring a number automatically makes it positive, there is no change to the graph of
j
(
x
)
.

::由于计算数字自动使其呈正数,j(x) 的图形没有变化。 -
k
(
m
(
x
)
)
=
|
√
x
|
:km(xx)) x
-
The graph looks the same as
m
(
x
)
.

::图形看起来与 m( x) 相同 。 -
m
(
k
(
x
)
)
=
√
|
x
|
::m(k(xx)) x -
The original square root graph is there, as well as its reflection across the
y
-axis.

::原始的平方根图就在那里, 以及它在Y轴上的反射。 -
r
(
p
)
=
1
,
000
−
1
4
(
30
−
25
p
)
2
=
-
156.25
p
2
+
375
p
+
775
:p)=1,000-14(30-25p)2=-156.25p2+375p+775
Section 2.13: Inverses of Functions
::第2.13节:职能的反面-
f
(
x
)
=
x
3

f - 1 ( x ) = 3 √ x

:xx) =x3 f-1 (x) = 3x
-
f
-
1
(
x
)
=
x
1
3
=
3
√
x
It is a function.
::f-1(x) =x13=3x 这是一个函数 。 -
f ( f − 1 ( x ) ) = x 1 3 ( 3 ) = x
::f( f- 1 (x)) =x13(3) =xf − 1 ( f ( x ) ) = x 3 ( 1 3 ) = x
::-1(f(xx))=x3(13)=x
::f( f- 1 (x)) =x13(3) =x f- 1 (f(x)) =x3( 13) =x -
g
(
x
)
=
√
x
,
x
≥
0

g - 1 ( x ) = x 2 , x ≥ 0

::g(x) x, x_0 g-1 (x) =x2, x_0 -
g
-
1
(
x
)
=
x
2
,
x
≥
0
It is a function.
::g- (x) =x2, x0, 这是一个函数 。 -
g
(
g
−
1
(
x
)
)
=
(
√
x
)
2
=
x
g − 1 ( g ( x ) ) = √ x 2 = x
::g( g- 1 (x)) = (x) 2=x g- 1 (g(x)) x2=x -
h
(
x
)
=
|
x
|

h - 1 ( x )

:hx) h-1 (x)
-
The inverse is
x
=
|
y
|
and is not a function.
::反之, x -
You can see from the graphs that they are inverses because they are symmetrical across the line
y
=
x
.
::您可以从图表中看到,它们是反向的,因为它们在横跨y=x线的对称。 -
j
(
x
)
=
2
x
−
5

j - 1 ( x )

:x)=2x-5j-1(x)
-
j
−
1
(
x
)
=
x
+
5
2
.
It is a function.
::j- 1(x)=x+52。这是一个函数。 -
j
(
j
−
1
(
x
)
)
=
2
(
x
+
5
2
)
−
5
=
x
+
5
−
5
=
x
j − 1 ( j ( x ) ) = ( 2 x − 5 ) + 5 2 = 2 x 2 = x
::j(j-1(xx))=2(x+52)=2(x+52)=5=x+5-5=xj-1(j(x))=(2x-5)+52=2x2=x -
The inverse is not a function since the function doesn't pass the horizontal line test.

::反向不是一个函数, 因为函数不会通过水平线测试 。 -
No. The inverse of
g
(
x
)
is
g
−
1
(
x
)
=
e
x
−
1
.
::否。 g(x) 的反义值是 g- 1(x) =ex- 1 。 -
You could switch the
x
- and
y
-coordinates given in the original table to make the table for the inverse.
::您可以切换原表格中给定的 x 和 Y 坐标, 使表格为反向 。 -
::F(0)=9/5(0)+32=32;F(100)=9/5(100)+32=9/5(100)+32=212b.C(F)=(F-32)*5/9c.F(C(F)=9/5((F-32)*5/9)+32=F和C(F(C))=(9/5C+32-32)*5/9
-
Domain:
x
∈
(
-
∞
,
∞
)
Range:
y
∈
[
-
1
,
1
]